Amazigh
Discovering the Different Amazigh Tribes
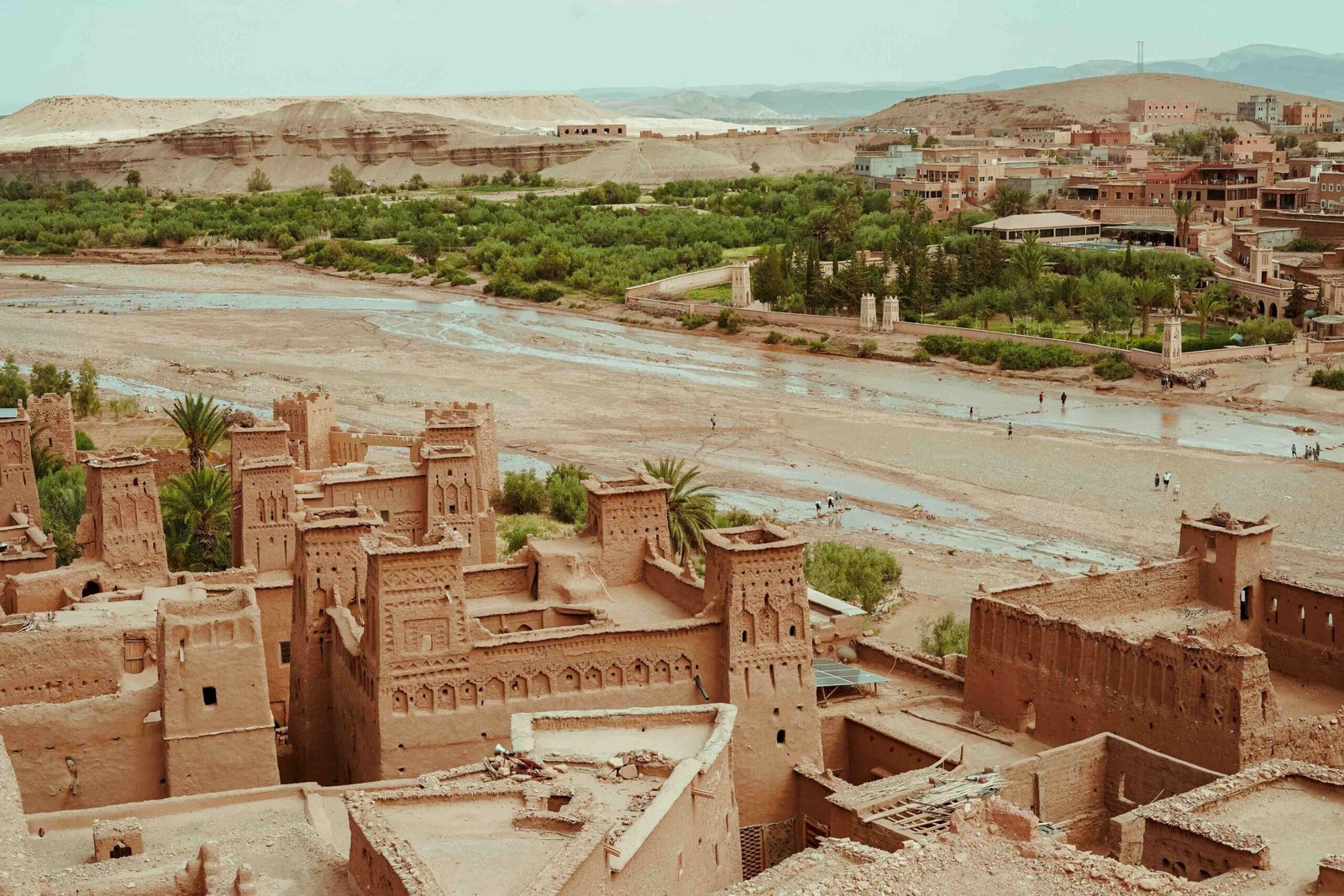

The Amazigh, or Berbers, are the indigenous people of North Africa, whose presence predates recorded history. Spread across Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and beyond, the Amazigh people are not a homogenous group but a rich tapestry of tribes, each with unique traditions, dialects, and lifestyles. Their unity lies in their shared cultural identity, while their diversity highlights the adaptability and resilience of their heritage.
This article explores the key Amazigh tribes, shedding light on their distinct characteristics and the shared cultural threads that connect them.
The Roots of Amazigh Identity
The term “Amazigh” means “free people,” reflecting their history of independence and their connection to the land. Despite centuries of foreign influence and colonization, the Amazigh people have preserved their language (Tamazight), customs, and traditions.
While the tribes vary in geography and lifestyle—some are nomadic, others settled in mountain villages or desert oases—they are united by their cultural symbols, such as Amazigh jewelry, textiles, and festivals.
Key Amazigh Tribes
1. The Riffians (Imazighen n Arrif)
The Riffians inhabit the Rif Mountains in northern Morocco. Known for their distinct dialect of Tamazight and vibrant music traditions, this tribe has contributed significantly to Amazigh cultural preservation.
The Riffians are also known for their craftsmanship, particularly in pottery and weaving. Their traditional festivals often feature rhythmic music and dance, showcasing their artistic heritage.
2. The Kabyle (Imazighen n Qbayel)
The Kabyle tribe, primarily located in northern Algeria, is one of the largest and most well-known Amazigh groups. They are renowned for their intricate jewelry-making, using silver and coral to craft elaborate designs.
Kabyle women play a central role in maintaining cultural traditions, excelling in pottery and weaving. Kabyle rugs, with their bold patterns, are highly sought after for their beauty and craftsmanship.
3. The Chleuh (Imazighen n Souss)
Located in Morocco’s Souss region, the Chleuh tribe is famous for their music and dance, particularly the ahwach, a group performance that combines rhythmic drumming and chanting.
The Chleuh people are also known for their agricultural skills, cultivating crops like olives and argan, which are integral to their cuisine and economy. Modern innovations, such as Amazigh food truck menus, often incorporate flavors inspired by Chleuh culinary traditions.
4. The Tuareg (Kel Tamasheq)
The Tuareg, also known as the “Blue People” due to their indigo-dyed clothing, are a nomadic tribe that roams the Sahara Desert. They are known for their unique language, Tamasheq, and their expertise in navigation and trade across vast desert landscapes.
Tuareg jewelry, characterized by its bold geometric designs, is highly symbolic and often carries spiritual meanings. Their festivals, featuring traditional music and poetry, are a celebration of their enduring connection to the desert.
5. The Zayanes
The Zayanes reside in the Middle Atlas Mountains of Morocco. This tribe is known for its resilience, having resisted colonial forces during the early 20th century.
Zayanes are skilled in weaving, producing beautiful rugs and textiles with intricate patterns. Their art and music reflect their mountainous environment and their deep connection to nature.
Shared Cultural Elements
Despite their differences, all Amazigh tribes share common cultural traits:
- Amazigh Women and Artisanship: Women are the custodians of Amazigh culture, excelling in crafts such as jewelry-making, weaving, and pottery. Their role is celebrated during festivals and communal gatherings.
- Festivals and Celebrations: Amazigh tribes hold vibrant festivals that showcase their music, dance, and traditional attire. Events like Yennayer, the Amazigh New Year, are celebrated across tribes.
- Advocacy and Modern Movements: Inspired by global movements like “Me Too” in Moroccan Amazigh communities, Amazigh women are increasingly using art and storytelling to advocate for gender equality and education.
The Importance of Preserving Amazigh Heritage
Efforts to preserve the diversity and unity of Amazigh tribes are essential for safeguarding their cultural legacy. Language preservation, support for artisans, and the promotion of Amazigh traditions through festivals and tourism are vital for keeping their identity alive.
As modern influences continue to shape their lives, the Amazigh people demonstrate remarkable adaptability, integrating their traditions into contemporary settings, from fashion to cuisine.
How to Experience Amazigh Culture
Visiting Amazigh regions offers a firsthand experience of their vibrant culture. Explore bustling markets, where you can purchase authentic Amazigh jewelry or handwoven textiles, or attend local festivals to immerse yourself in their music and dance.
Supporting Amazigh artisans by purchasing their crafts not only sustains their livelihood but also helps preserve their traditions for future generations.
Final Thoughts
Discovering the different Amazigh tribes reveals a fascinating world of cultural richness and diversity. Each tribe, with its unique traditions, adds to the vibrant mosaic of Amazigh identity.
By learning about and celebrating Amazigh culture, we honor their resilience and contribute to the preservation of a heritage that has enriched North Africa and inspired the world.