Amazigh
Defining Amazigh Identity in Today’s World
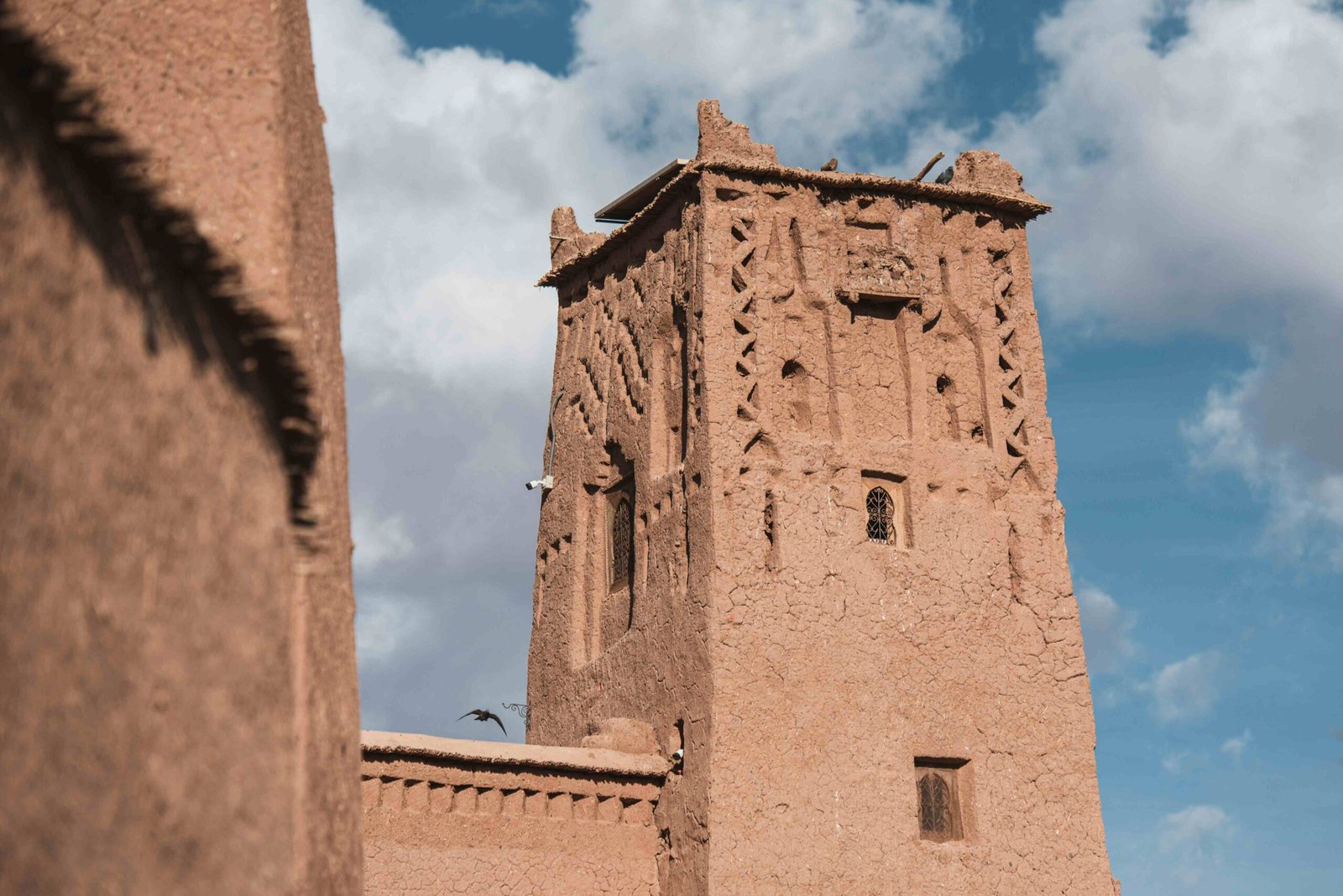

The Amazigh people, also known as Berbers, are the indigenous inhabitants of North Africa. Spanning countries like Morocco, Algeria, Libya, and Tunisia, the Amazigh have a rich history and cultural heritage that continues to thrive despite centuries of marginalization. Today, the Amazigh identity is being redefined as communities work to preserve their language, traditions, and rights in a rapidly changing world.
This article explores what it means to be Amazigh in the modern era, delving into their history, cultural expressions, and efforts to sustain their identity.
Who Are the Amazigh?
The Amazigh, whose name means “free people” in Tamazight, have lived in North Africa for thousands of years. Their culture is characterized by:
- Unique Dialects: Varieties of the Tamazight language, such as Tachelhit, Kabyle, and Tarifit.
- Distinct Art: Amazigh crafts like pottery, rugs, and jewelry often feature geometric patterns and symbols.
- Strong Community Values: A focus on family, solidarity, and respect for nature.
The Struggles and Triumphs of Amazigh Identity
Historical Challenges
For much of their history, the Amazigh faced cultural suppression. Colonization, Arabization, and post-independence policies in North African countries often marginalized their language and traditions.
Modern Recognition
Recent years have seen significant strides in Amazigh rights:
- Language Recognition: Tamazight is now an official language in Morocco and Algeria.
- Cultural Revival: Festivals, music, and art celebrating Amazigh heritage are gaining global recognition.
- Advocacy Movements: Initiatives like the “Me Too in Moroccan Amazigh” movement amplify Amazigh women’s voices in cultural and social issues.
Key Elements of Amazigh Identity
1. Language
Language is a cornerstone of Amazigh identity. Dialects like Tachelhit, Kabyle, and Tarifit not only serve as communication tools but also carry the values and wisdom of the community. Efforts to preserve these languages include teaching them in schools and using the ancient Tifinagh script in public signage.
2. Art and Crafts
Amazigh crafts are more than decorative items; they are a form of storytelling. Symbols in jewelry, rugs, and pottery often represent natural elements, spiritual beliefs, or social status. For example:
- Triangles: Represent mountains.
- Zigzags: Symbolize water or protection.
- The Eye: A motif for warding off evil.
3. Food
Amazigh cuisine reflects their connection to the land. Staples like couscous, tagine, and flatbreads are flavored with local spices. Even modern innovations, such as the Amazigh food truck menu, showcase the community’s adaptability and creativity.
4. Music and Dance
Traditional Amazigh music, featuring instruments like the bendir and gimbri, is often accompanied by rhythmic dances. These performances are integral to festivals and communal gatherings, reflecting themes of love, resistance, and celebration.
5. Women’s Roles
Amazigh women are central to preserving traditions. From passing down folk tales to creating intricate crafts, their contributions are invaluable. Movements advocating for women’s rights within the Amazigh community are gaining momentum, addressing gender equality while celebrating their cultural significance.
Challenges to Amazigh Identity in the Modern World
While there has been progress, challenges remain:
- Urbanization: As younger generations move to cities, there’s a risk of losing rural traditions and languages.
- Globalization: Western influences can overshadow local customs.
- Political Issues: Advocacy for Amazigh rights can sometimes face resistance from governments.
Preserving and Promoting Amazigh Identity
Education and Language Preservation
Introducing Tamazight into school curricula ensures that future generations remain connected to their roots.
Cultural Festivals
Events like Yennayer (Amazigh New Year) highlight the community’s traditions, attracting both locals and global audiences.
Global Awareness
Social media platforms are powerful tools for spreading knowledge about Amazigh culture. Sharing stories, crafts, and historical insights helps keep the heritage alive.
The Global Relevance of Amazigh Identity
In a world that values diversity, the Amazigh identity offers a unique perspective on resilience and cultural pride. By embracing their heritage, the Amazigh not only enrich their communities but also contribute to the global tapestry of indigenous cultures.
Conclusion
Defining Amazigh identity in today’s world means striking a balance between preserving ancient traditions and adapting to modern realities. Through their language, art, and activism, the Amazigh demonstrate that cultural heritage is not static but ever-evolving.
As the Amazigh people continue to celebrate their identity, they inspire others to value and protect the richness of their own cultural roots. Their story is one of perseverance, creativity, and pride, making the Amazigh identity a beacon of hope and resilience in the modern world.