Culture
Cultural Resource Management: Preserving Our Heritage
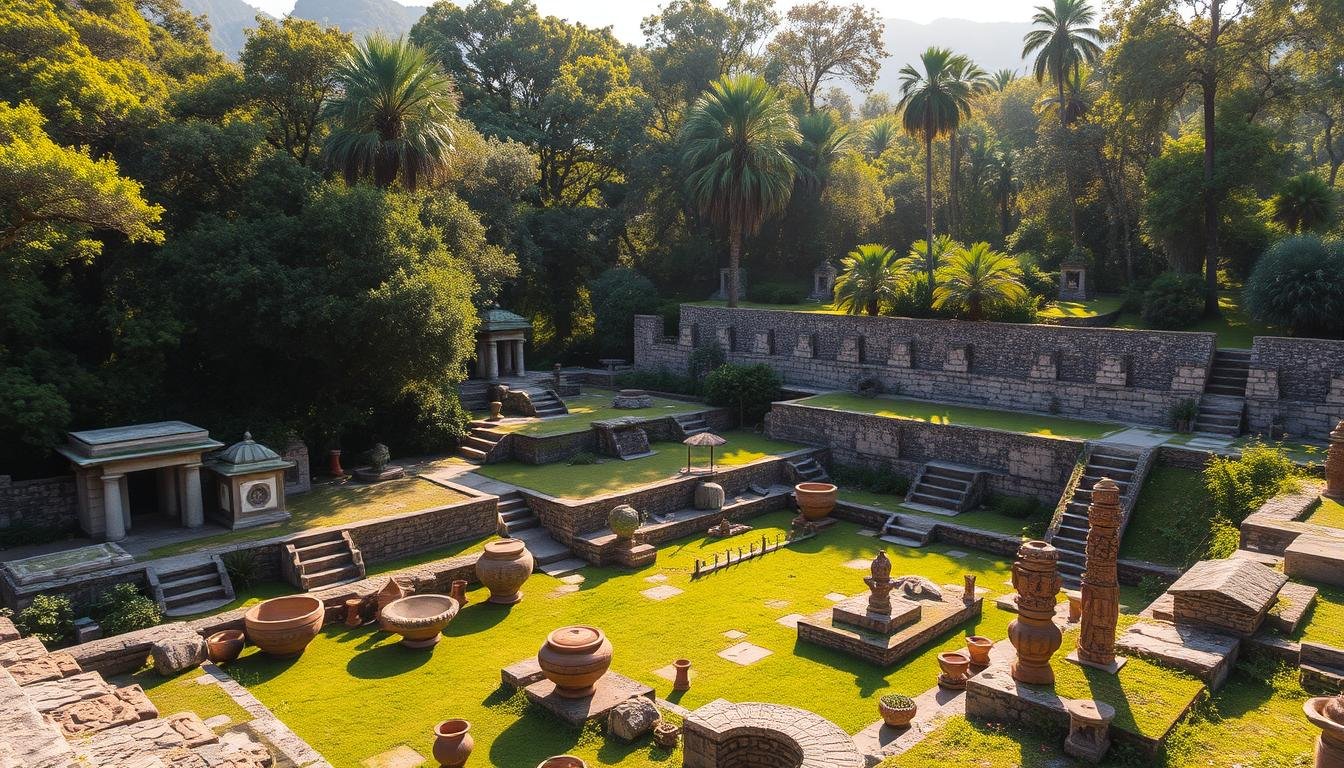

In today’s fast-changing world, saving our cultural heritage is more important than ever. Cultural resource management (CRM) is all about finding, checking, and keeping safe the things that tell our history. This includes old ruins and the traditions that make our communities unique. CRM helps make sure we keep the stories of human history alive for future generations.
CRM brings together many fields, like archaeology, history, anthropology, and conservation. These experts dig into the past through sites, artifacts, and traditions. They work hard to share these stories with us today and show their importance in our world now. By doing research, conservation, and working with communities, they aim to save the cultural treasures that define us all.
Key Takeaways
- Cultural resource management is a multidisciplinary field dedicated to preserving historical sites, artifacts, and traditions.
- It involves the collaborative efforts of archaeologists, historians, anthropologists, and conservation scientists.
- CRM plays a crucial role in safeguarding our collective heritage for future generations.
- By understanding the historical significance of cultural resources, CRM professionals work to protect and conserve them.
- Effective CRM practices help to foster a deeper appreciation for the rich diversity of human experiences and achievements.
Understanding Cultural Resource Management: A Comprehensive Overview
Cultural resource management is a field that deals with preserving and understanding our shared heritage. It focuses on studying and caring for cultural resources. These can be physical things like old buildings or intangible things like traditions.
Types of Cultural Resources
Cultural resources fall into two main categories:
- Tangible Heritage: This includes physical items like buildings, artifacts, and art.
- Intangible Heritage: This includes things like stories, dances, and crafts that are passed down.
Historical Significance in Modern Context
Cultural resources are more than just old things. They help us understand our past and guide us today. By studying and saving these resources, we learn about history and use that knowledge to solve today’s problems.
Key Management Principles
Good management of cultural resources follows a few key rules:
- Preservation: Keeping cultural resources safe for future generations.
- Interpretation: Teaching people about cultural heritage through education and events.
- Sustainable Management: Creating plans to protect cultural resources for a long time.
By following these principles, managers help keep our history alive and connect people with their cultural roots.
“Cultural resource management is not just about preserving the past, but about shaping the future.”
The Evolution of Heritage Preservation Through Time
The journey of preserving cultural heritage is long and fascinating. It began with the early days of antiquarianism. Over time, the field of heritage preservation history has grown. It has been shaped by the hard work of many and the changing needs of people everywhere.
In the 18th and 19th centuries, a growing love for history sparked the conservation movements. Scholars and fans worked hard to save historical items and places. Leaders like John Ruskin and William Morris fought to keep buildings and monuments safe. They set the stage for today’s cultural protection timeline.
“The past is not a vanished country from which we are forever exiled, but a continuing presence in our lives, a place where we can return with imagination, curiosity, and care.”
The 20th century brought big changes to how we protect heritage. UNESCO and other groups helped create global rules for saving cultural treasures. Events like the 1972 World Heritage Convention helped spread the word and guide efforts at the national level.
- The rise of the heritage preservation history movement in the 19th century, spearheaded by figures like Ruskin and Morris.
- The establishment of international organizations, such as UNESCO, and their role in shaping cultural protection timeline.
- The pivotal 1972 World Heritage Convention and its impact on global conservation movements.
Today, the field of cultural resource management keeps growing. It now uses new tech, works with communities, and focuses on sustainable ways to protect our shared heritage preservation history for the future.
Legal Frameworks and Regulatory Guidelines in Heritage Protection
The protection of cultural resources is covered by a wide legal framework. This framework includes federal, state, and international levels. The National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA) is a key U.S. law since 1966.
Federal Preservation Laws
The NHPA created the National Register of Historic Places. It lists sites of national, state, and local importance. It also requires federal agencies to think about how their actions affect historic sites.
Other federal laws, like the Archaeological Resources Protection Act and the Native American Graves Protection and Repatriation Act, add more protection for cultural resources.
State-Level Regulations
States also have their own preservation laws and rules. These state laws add to the federal framework. They help protect historic buildings, archaeological sites, and cultural landscapes in their areas.
International Treaties and Conventions
The UNESCO World Heritage Convention is a major global agreement. It protects sites of great universal value. The Hague Convention for the Protection of Cultural Property and the Burra Charter also guide heritage preservation worldwide.
| Legal Framework | Key Provisions | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA) | Established the National Register of Historic Places, mandates federal agency review of impacts on historic properties | Federal |
| UNESCO World Heritage Convention | Identifies and conserves sites of outstanding universal value | International |
| State Preservation Laws | Provide additional layers of protection for historic resources within state jurisdictions | State |
These legal frameworks and guidelines are key to protecting our cultural heritage. They ensure that preserving historical resources is a priority at all levels of government.
Digital Technologies in Cultural Resource Management
Digital technologies have changed how we save and show our shared history. They help us document historic sites and scan artifacts in 3D. These tools have made archaeology and saving heritage much better.
GIS in archaeology is a big step forward. It lets researchers map and study cultural sites with great detail. This way, they can make better choices about how to protect and manage these sites.
Virtual reconstruction is also a game-changer. It uses 3D models and augmented reality to let people explore history in new ways. This makes learning about the past fun and interactive.
These digital tools have made sharing our cultural heritage easier. They help create virtual tours and interactive exhibits. This way, we can all experience history in a new and exciting way.
“The integration of digital technologies in cultural resource management has unlocked new avenues for preserving, exploring, and sharing our global heritage.”
As we keep working to save our cultural heritage, digital tools will be key. They help us document, scan, map, and rebuild our history. This ensures our cultural treasures are safe and appreciated for years to come.
Stakeholder Engagement and Community Participation
Effective cultural resource management needs a team effort. It involves working with many groups, like local communities and indigenous peoples. This way, we can better understand our shared heritage and help communities protect it.
Indigenous Communities’ Role
Indigenous communities have deep knowledge about their ancestral lands. It’s key to include their indigenous heritage in our work. This makes our community archaeology efforts more respectful and effective.
Public-Private Partnerships
Good cultural resource management often comes from public-private partnerships. Working together with government, non-profits, and private companies helps us achieve more. It leads to better heritage education and public involvement.
Educational Outreach Programs
It’s important to reach out to the public through education. We can do this through school programs, community workshops, and online platforms. This way, we teach people about our shared history and encourage them to protect it.
| Stakeholder Engagement Strategies | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Collaborative workshops with indigenous communities | Integrate traditional knowledge, promote cultural sensitivity |
| Partnerships with local heritage organizations | Leverage expertise, amplify outreach efforts |
| Comprehensive public education campaigns | Raise awareness, foster community stewardship |
“Engaging local communities, especially indigenous groups, is not just a matter of public relations—it is fundamental to the long-term success of cultural resource management.”
By working together and including everyone, we can protect our heritage. We also empower diverse communities to help preserve and care for it.
Assessment and Documentation Methods
In the world of cultural resource management, it’s key to assess and document our heritage. This includes surveys, documentation, condition checks, and managing inventories. These steps are vital for keeping our history safe.
First, we do cultural resource surveys to find and value historical sites and artifacts. We use field work, archives, and detailed data to understand these resources. This helps us see their importance and how they fit into our culture.
Next, we document cultural assets in full. This means taking photos, making drawings, and writing reports. It gives us a clear picture of what we have today. This info helps us track changes and plan for the future.
Then, we do condition assessments to check how well these resources are doing. We look at their state, any damage, and what might harm them. This helps us create plans to keep them safe.
Finally, we use inventory management to keep track of our cultural treasures. This system helps us monitor and make decisions about preservation. It’s key for protecting our heritage for the long haul.
| Technique | Purpose | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Cultural Resource Surveys | Identify and evaluate historical sites, artifacts, and cultural resources | Provide a comprehensive understanding of the cultural landscape and inform preservation efforts |
| Site Documentation | Create detailed records of cultural heritage assets | Enable long-term monitoring and informed decision-making for conservation |
| Condition Assessments | Evaluate the physical integrity and deterioration of cultural resources | Inform targeted conservation strategies and prioritize preservation needs |
| Inventory Management | Catalog and organize data on cultural heritage assets | Facilitate efficient tracking, monitoring, and decision-making for long-term preservation |
By using these important methods, we can protect and value our cultural heritage. This way, we ensure it’s safe for future generations to enjoy.
Challenges in Modern Heritage Conservation
Preserving our cultural heritage is getting harder. Climate change and urban growth are major threats. These challenges make protecting our treasured sites very complex.
Climate Change Impact
Climate change is a big worry for heritage conservation. Rising seas and extreme weather harm historic sites worldwide. The heritage at risk is clear as cultural treasures face damage or loss.
Urban Development Pressures
Fast urban growth is another big challenge. Urban encroachment on historic areas threatens cultural assets. It’s hard to balance development needs with preserving our heritage.
Resource Allocation Issues
Finding enough conservation funding is tough. With limited money, choosing which sites to save is hard. It’s also important to protect cultural practices and traditions.
To overcome these challenges, we need a team effort. Experts from government, non-profits, local groups, and businesses must work together. By tackling climate change effects, urban development pressures, and resource allocation issues, we can save our cultural heritage for the future.
Best Practices in Site Management and Preservation
Managing and preserving cultural heritage sites is key to protecting our shared history and identity. A good approach includes making strong heritage management plans, using preventive conservation, and balancing public access with preservation needs.
Creating detailed heritage management plans is a crucial strategy. These plans outline how to maintain, protect, and enhance a site’s cultural value. They cover routine checks, maintenance, and steps to tackle potential threats.
Preventive conservation is vital for keeping cultural resources safe. It involves steps like controlling the environment, managing visitors, and using the right conservation methods. This way, we can prevent damage and extend the life of cultural items.
It’s also important to balance visitor management with preservation. This means finding a way to let people visit while keeping the site safe for the future. This might include setting visitor limits, creating educational programs, and promoting eco-friendly tourism.
By following these best practices in site conservation, we can protect cultural resources for future generations. This ensures they remain valuable and accessible for years to come.
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Heritage Management Plans | Comprehensive plans that outline protocols for maintenance, protection, and enhancement of cultural significance |
| Preventive Conservation | Measures to minimize damage and deterioration, such as environmental control and proactive interventions |
| Visitor Management | Strategies to balance public access with preservation needs, including capacity limits and sustainable tourism practices |
“Preserving our cultural heritage is not just about safeguarding the past, but also about shaping the future we want to build.”
Sustainable Approaches to Cultural Resource Management
The world is waking up to the need for environmental care. Cultural resource management is now using sustainable methods. This includes eco-friendly conservation and new economic models. These steps help keep our heritage sites safe for the future.
Green Conservation Methods
Cultural resource managers are using sustainable conservation to lessen environmental harm. They choose renewable materials and energy-saving tech. They also focus on waste management to protect our history and the planet.
Economic Sustainability Models
Keeping cultural resources financially stable is key. New heritage economics models are being tried. They use adaptive reuse and partnerships to make sites financially strong. This way, sites can stand on their own, not just rely on government or donations.
Long-term Preservation Strategies
Keeping cultural resources safe for the long haul needs a big plan. Long-term preservation strategies include planning for risks and disasters. They also involve regular upkeep. This way, we can protect these treasures for generations to come.
| Sustainable Conservation Practices | Economic Sustainability Models | Long-term Preservation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
“Sustainable cultural resource management is not just about preserving the past; it’s about ensuring a brighter future for our shared heritage.”
Conclusion
Cultural resource management is key to saving our shared heritage. It involves understanding different cultural resources and using new technologies. Dedicated professionals work hard to protect our past.
The future of heritage preservation is both challenging and full of opportunities. Climate change, urban growth, and funding issues will test our cultural heritage. But, with new ideas, better partnerships, and a strong focus on cultural resource management importance, we can overcome these hurdles. This way, our heritage conservation legacy will last for many years.
We can make a difference by using green practices, digital tools, and working together. This will help us keep and celebrate our cultural heritage. As we go forward, let’s keep working to save our cultural treasures. This way, their stories will continue to enrich and shape our world.
FAQ
What is cultural resource management?
Cultural resource management is about keeping cultural heritage safe for the future. It includes historical sites, artifacts, and traditions. Experts from archaeology, history, anthropology, and conservation science work together in this field.
Why is cultural resource management important?
It’s vital for keeping our heritage alive for future generations. It makes sure historical and cultural treasures are safe and available for everyone. This helps keep their true value and meaning in today’s world.
What types of cultural resources are managed?
Many things are managed, like old buildings, landscapes, and traditions. Also, historical artifacts and archaeological sites are part of it.
How has the field of heritage preservation evolved over time?
It has grown from simple collecting to a detailed science. Important steps include the rise of conservation efforts and the creation of key organizations. International agreements have also played a big role in protecting our cultural treasures.
What are the legal frameworks and regulatory guidelines in heritage protection?
Laws and rules from the federal, state, and international levels guide it. The National Historic Preservation Act and UNESCO’s World Heritage Convention are key examples.
How are digital technologies transforming cultural resource management?
New tech like 3D scanning and GIS mapping is changing how we save and share heritage. These tools make it easier to preserve and understand our cultural past.
What is the role of stakeholder engagement and community participation in cultural resource management?
Working with local communities, especially indigenous groups, is essential. It builds awareness and ownership. This helps in keeping heritage efforts going strong over time.
What are some of the key challenges in modern heritage conservation?
Today, we face issues like climate change and urban development. Finding enough money and resources for conservation is also a big challenge.
What are the best practices in cultural resource site management and preservation?
Good practices include making detailed plans and using preventive care. It’s also important to balance keeping sites safe with letting people visit and learn.
How can cultural resource management be approached in a sustainable manner?
Sustainable management uses green conservation methods and finds ways to make heritage sites financially stable. It also focuses on long-term strategies to keep cultural resources relevant and accessible.