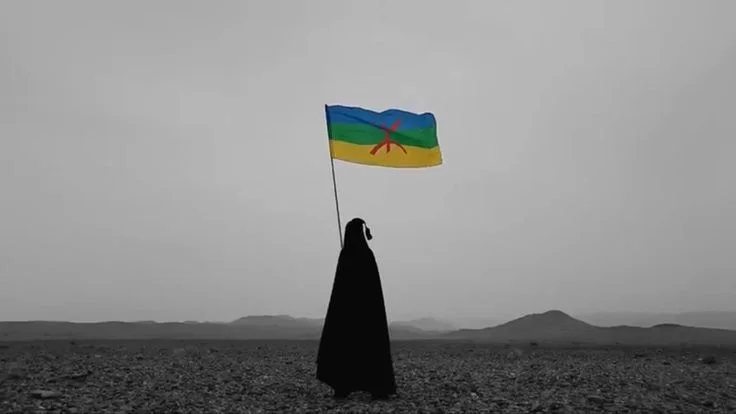
Amazigh
Exploring the Powerful Impact of the Amazigh on African History

Introduction
The study of African history would be incomplete without an examination of the Amazigh people. Known also as the Berbers, the Amazigh have played a crucial role in shaping the continent’s history through their cultural, political, economic, and religious contributions. This essay explores the multifaceted impact of the Amazigh on African history, starting with their origins and identity, extending through their political and economic contributions, and culminating in their influence on culture, religion, and their modern-day challenges.
The Origins and Identity of the Amazigh
Historical roots and early settlements
The origins of the Amazigh people can be traced back to prehistoric times. Archaeological evidence suggests that they have inhabited North Africa for thousands of years, long before the arrival of the Phoenicians, Romans, and Arabs. The cave paintings in Tassili n’Ajjer, Algeria, dating back to 10,000 BC, are among the earliest indicators of Amazigh presence. Early historical accounts, including those by ancient Egyptian and Greek historians, also mention the Amazigh, providing a glimpse into their early settlements and social structures.
Cultural and linguistic characteristics
The Amazigh culture is rich and diverse, characterized by unique linguistic and artistic traditions. The Tamazight language, with its various dialects, is one of the most defining aspects of Amazigh identity. It belongs to the Afro-Asiatic language family and has its own script, Tifinagh, which has been used for centuries. Culturally, the Amazigh are known for their traditional music, dance, and oral literature, which have been preserved through generations. Their art, symbolized by intricate jewelry, textiles, and pottery, reflects a blend of indigenous and external influences.
Geographic distribution across Africa
Geographically, the Amazigh are mostly concentrated in North Africa, spanning countries such as Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Mali, and Niger. Despite this concentration, their influence extends beyond these regions due to historical migrations and trade routes. The Saharan trade routes facilitated their spread into sub-Saharan Africa, allowing the Amazigh to interact and integrate with various African societies. This geographic distribution has contributed to the diverse nature of their society and their impact on African history.
Political Contributions of the Amazigh
Role in ancient African empires
The Amazigh have played vital roles in some of Africa’s most prominent ancient empires. In Carthage, an empire founded by the Phoenicians but largely influenced by the Amazigh, they served as both leaders and soldiers. The Kingdom of Numidia, under the leadership of King Masinissa, is another notable example. Masinissa is credited with unifying various Amazigh tribes and establishing a powerful kingdom that played a crucial role in the Punic Wars alongside Rome.

Influence in regional politics
Beyond ancient empires, the Amazigh have had a lasting influence on regional politics throughout history. During the Middle Ages, Amazigh dynasties such as the Almoravids and Almohads ruled large parts of North Africa and even extended their control into Spain and Portugal. These dynasties not only established powerful states but also promoted significant cultural and intellectual advancements. The role of the Amazigh in more recent North African political movements, including the fight for independence from colonial powers, further underscores their political significance.
Notable Amazigh political leaders
History is replete with notable Amazigh political figures whose decisions and leadership have shaped African history. Queen Dihya, also known as Kahina, is celebrated for her fierce resistance against the Arab invasions in the 7th century. Muammar Gaddafi, the former leader of Libya, although controversial, was of Amazigh descent and played a pivotal role in modern African politics. The legacy of these leaders demonstrates the enduring political presence of the Amazigh people.
Economic Influence of the Amazigh
Trade routes and commerce
The economic contributions of the Amazigh are significant, particularly in the context of historical trade routes and commerce. The Trans-Saharan trade routes, established and maintained by the Amazigh, facilitated the exchange of goods such as gold, salt, and ivory between North Africa and sub-Saharan Africa. They also transported cultural and intellectual ideas along these routes, contributing to the spread of knowledge and technology across regions.
Agricultural practices and innovations
Agriculturally, the Amazigh have introduced and refined various farming techniques that have had lasting impacts on regional economies. They are known for terrace farming and irrigation methods that make the best use of arid and semi-arid landscapes. These innovations have not only supported their own communities but have also influenced agricultural practices throughout North Africa and beyond.
Contributions to regional economies
In addition to their agricultural and trade contributions, the Amazigh have been integral to the development of crafts and industries. Their skills in metalwork, leatherwork, and textile production created thriving markets and contributed to the fame of North African goods. These economic activities have provided a foundation for regional economies and facilitated interactions with other cultures and civilizations.
The Amazigh in African Art and Culture
Traditional music and dance
The cultural contributions of the Amazigh are perhaps most vividly seen in their art and traditions. Traditional Amazigh music and dance are integral to their cultural heritage, often performed during festivals and significant life events. Instruments such as the bendir (a type of drum) and the guembri (a stringed instrument) are central to their musical expression. The rhythmic and melodic structures of Amazigh music have influenced broader African music traditions, contributing to the continent’s rich musical tapestry.
Influence on visual arts and crafts
The visual arts, including pottery, weaving, and jewelry-making, are another domain where Amazigh culture shines. Amazigh crafts are distinguished by their intricate geometric patterns and symbolic motifs, which often carry spiritual and cultural significance. These artistic traditions have been passed down through generations, preserving the Amazigh identity while also inspiring contemporary African art. The Amazigh influence can be seen in the decorative arts of neighboring regions, reflecting a blend of styles and techniques.

Preservation and celebration of heritage
The preservation and celebration of Amazigh heritage are ongoing efforts that highlight the resilience and pride of the Amazigh people. Festivals, such as the annual Imilchil Marriage Festival in Morocco, celebrate Amazigh traditions and bring communities together. Cultural organizations and activists are working to preserve the Tamazight language and promote Amazigh cultural expression in modern contexts. These efforts ensure that the rich cultural legacy of the Amazigh continues to thrive amidst contemporary challenges.
The Amazigh and African Religious History
Traditional beliefs and spiritual practices
Religiously, the Amazigh have a diverse and dynamic spiritual history. Traditionally, they practiced animism, worshiping gods and spirits associated with natural elements and ancestral figures. These beliefs were rooted in a deep reverence for the natural world and were expressed through rituals, festivals, and artistic symbols.
Interaction with Islam and Christianity
The advent of Islam and Christianity brought significant changes to Amazigh spiritual practices. Many Amazigh communities embraced Islam, contributing to the spread of the religion across North Africa. Sufi traditions, in particular, found a prominent place within Amazigh culture, blending with pre-existing spiritual practices. There were also Amazigh who converted to Christianity, especially during periods of Roman and Byzantine influence. The interaction between these major world religions and traditional Amazigh beliefs created a unique religious syncretism that persists to this day.
Religious festivals and rituals
Religious festivals and rituals among the Amazigh reflect this blend of traditions. For instance, the celebration of Eid al-Adha carries distinct Amazigh elements, incorporating local customs and foods. The Sebeiba Festival in Algeria’s Sahara, celebrated by the Tuareg (a nomadic Amazigh group), is another example where pre-Islamic practices blend with Islamic traditions. These festivals and rituals not only enrich the religious landscape but also serve to strengthen community bonds and cultural identity.
Modern Challenges and Revival Efforts
Issues of political marginalization
In modern times, the Amazigh have faced significant challenges, particularly issues of political marginalization. Post-independence national movements in North African countries often sought to promote a homogeneous Arab identity, sidelining Amazigh cultural and linguistic rights. This marginalization has led to socio-economic disadvantages for many Amazigh communities and has spurred movements aiming to reclaim their rights and recognition.
Movements for cultural preservation
In response to cultural and political marginalization, various Amazigh movements have emerged. Organizations like the World Amazigh Congress advocate for the preservation and promotion of Amazigh language and culture. Educational initiatives, such as the inclusion of Tamazight in school curricula and the promotion of Amazigh literature, are central to these efforts. The revival of traditional arts and festivals also plays a crucial role in maintaining cultural heritage.
Impact of globalization on Amazigh identity
Globalization presents both challenges and opportunities for Amazigh identity. On the one hand, it brings increased awareness and solidarity among Amazigh communities globally. On the other hand, exposure to global cultural trends can lead to cultural dilution and loss of traditional practices. Balancing the preservation of Amazigh heritage with the inevitabilities of modernity is an ongoing challenge that requires innovative and dedicated approaches.
Conclusion
The Amazigh have undeniably left an indelible mark on African history. From their ancient origins and distinct cultural identity to their significant political, economic, and religious contributions, the Amazigh have shaped the African continent in profound ways. Despite modern challenges, efforts to preserve and revive Amazigh culture continue, ensuring that their rich heritage remains an integral part of Africa’s diverse historical tapestry. Understanding and appreciating the Amazigh’s impact not only enriches our knowledge of African history but also highlights the importance of cultural diversity and resilience in shaping human civilization.